Are you parents and looking for information regarding congenital cataract?
In this article we have discussed about congenital cataract and highlighted the information which every parents need to know for healthier vision of their child.
In the human eye, the retina plays a vital role in image formation. Light strikes the lens and passes to the retina. This phenomenon helps us to see. The lens of our eye should be clear to bend or refract the light properly.
If the lens contains any cloudiness, it will blur the vision and may lead to permanent blindness. This condition is normally known as a cataract. It usually occurs in the eyes of adults or elderly people.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a congenital cataract?
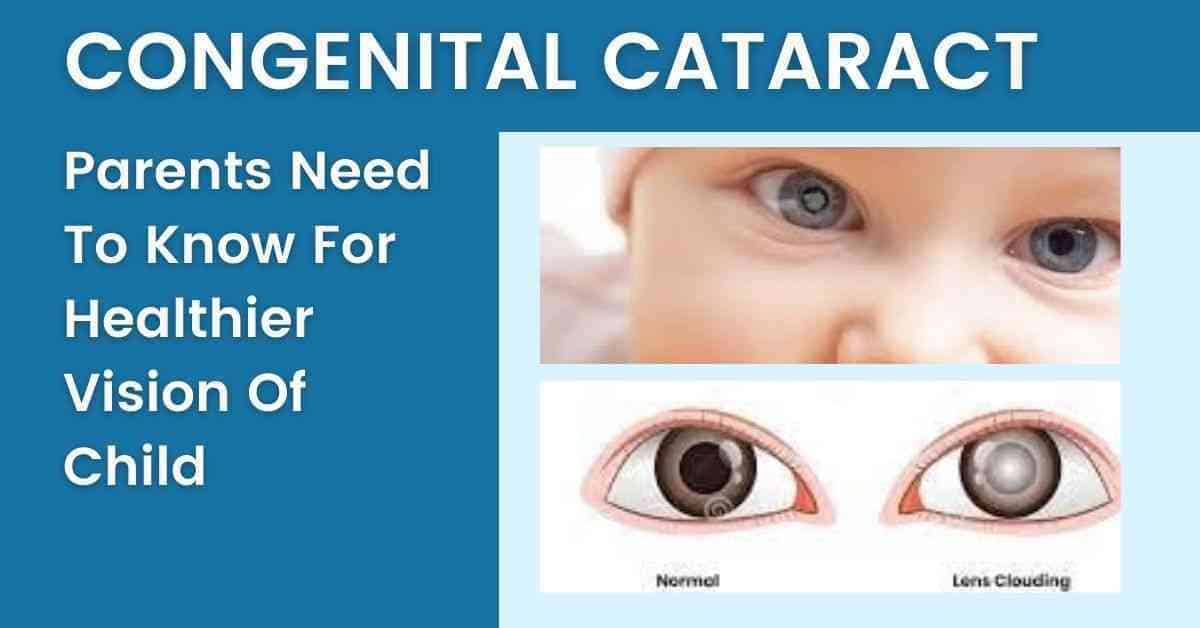
If this cloudiness happens in a newly born baby or the first year of his life, it will be known as a congenital cataract. One-third of congenital cataracts are hereditary eye diseases. If this cataract remains unfound in infants, it can lead to permanent blindness.
Depending upon the density, it is imperative to eliminate the congenital cataract as early as possible to avoid the permanent loss of vision.
What are the types of congenital cataracts?
Congenital cataracts are of two types:
- Syndromic Congenital Cataract
- Non Syndromic Congenital Cataract
Syndromic Congenital Cataract
Congenital cataract becomes syndromic when it occurs with various other diseases. For example, it happens with different types of mutations, including chromosomal abnormalities, loss-of-heterozygosity, mitochondrial disorders, or with more complex genetic disorders such as diabetes.
Non-Syndromic Congenital Cataract
Congenital cataracts will be non-syndromic if this is the only condition the newly born is suffering from. In non-syndromic congenital cataract lens is the only compromised part.
Symptoms of congenital cataracts
It is very difficult to detect congenital cataracts. To find the baby is suffering from a congenital cataract or not, the best way is to consult the ophthalmologist. He will examine the baby and noticed the symptoms.
Usually, there are various symptoms of congenital cataracts in babies depending upon where and how much cloudiness is present in the lens, and whether it is in one eye or both eyes.
What are the major signs and symptoms of congenital cataracts?
The major symptoms of congenital cataracts are as follow:
Unaware of surroundings
One of the common symptoms is that baby is completely unaware of its surroundings. He doesn’t show proper and appropriate response to any movement and action. It usually happens when the baby has cataracts in both eyes. In this situation, minutely observe your baby’s reflexes and take timely advice from your ophthalmologist.
The unusual color of the pupil
Another common symptom of congenital cataracts is the unusual color of the eye. On observing the pupil of the baby, if you see a grey or white color spot in the eyes, other than normal black color, it is a sign of worry and you should consult the ophthalmologist immediately.
In some cases, instead of a spot, there is a dense layer covering the entire pupil.
Lack of red-eye glow
If you see the photo of your baby, you’ll observe the missing “red-eye glow” in the eyes. Rather you see a white cataract in the eyes. It can be a symbol of a congenital cataract.
Abnormal Eye Movement/ Nystagmus
Nystagmus or uncontrolled movement of the eye is another symptom of a congenital cataract. In this situation, the eye produces a wobbling effect, or in simple words eye has side to side or up and down uncontrolled movement.
Squint/Unaligned eyes
In various cases, ophthalmologists observe the baby has an uneven pattern or nonaligned eyes. This may be one of the symptoms and it is known as squint.
You should keep one thing very clear in your mind congenital cataracts may occur in one or both eyes. You should make a complete frequent inspection of the eyes of your baby very closely by the ophthalmologist, in the first 72 hours. After that, manage this eye check-up with other routine examinations.
If you observe any of the above symptoms in your child, do timely consultation with an ophthalmologist, to avoid any inconvenience.
Causes of Congenital Cataracts
There are various causes of congenital cataracts, including genetic causes, any infections, drug reactions, or any other. On the other hand, there are still some cases of congenital cataracts in which you cannot point out any specific reason or cause for congenital cataracts.
What is the reason for congenital cataracts?
Following are some causes of congenital cataracts:
Gene mutation
Gene mutation is one of the reasons for congenital cataracts in newly born babies. In the gene mutation process, parents pass some faulty genes to their offspring. This faulty gene disturbs the normal sequence of the chromosome
Chromosomes are the basic structure present in the cells of the body which convey genetic messages in the form of genes.
Consequently, this mutation hinders the normal and healthy lens development of the eye and cause congenital cataract.
Due to birth defects
In some cases, the congenital cataract may occur due to some birth defects. For example Chondrodysplasia syndrome, Conradi-Hünermann syndrome, Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Ectodermal dysplasia syndrome, Familial congenital cataracts, Hallermann-Streiff syndrome, Lowe syndrome, Marinesco-Sjögren syndrome, Pierre-Robin syndrome, and Trisomy 13.
Trauma during pregnancy
If a mother got any physical damage or injury by any sort of accident, domestic violence, or from any other source it can harm the baby in the womb of the mother. This shock may become a cause of various abnormalities in a baby including congenital cataracts.
Hypoglycemia/Diabetes
Too much high level of glucose in the blood may cause diabetes and a low level of glucose may cause hypoglycemia. Both have a bad impact on the organs of the mother, particularly her kidneys and nerves. Subsequently, it can affect the baby’s health.
Contagions in pregnancy
Congenital cataracts can ensue when the mother gets infected by diseases like herpes viruses, chickenpox, or cytomegalovirus. Some other infections are influenza, measles, polio, rubella, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, etc. which are also included in the list of infections that can rise the danger of congenital cataracts in babies.
Radiation treatment
In certain circumstances, if a mother undergoes any sort of radiation treatment or exposure i.e., x-rays, etc. It will become one of the reasons for congenital cataracts in infants.
Drug/Steroids Reaction
Overexposure or reaction of any drug in the mother during pregnancy can increase the risk of congenital cataracts in the baby. For an instance, tetracycline antibiotics used to treat contagions in pregnant females have caused cataracts in newborn babies. Similarly, corticosteroids are also involved in some cases.
Diagnosis of congenital cataracts
Following are the recommended diagnosis steps for congenital cataract:
Eye examination
Sometimes doctors identify congenital cataracts through the complete examination of newly born. That’s the reason that doctors recommend comprehensive eye inspection as early as possible after the birth of the baby. This checkup helps detect congenital cataracts and is useful in diagnosing other abnormalities.
Red reflex test
This test is carried out in a dark room or surroundings. The bright light of the ophthalmoscope is used in this test from a distance of 1-2 ft. This test is also very beneficial in spotting glaucoma, retinoblastoma, and some other diseases.
Retinoscopy
Retinoscopy is very helpful to observe the undilated pattern of the pupil. When light is low your pupil opens up or dilate. Likewise, it gets smaller when the light is bright. So, retinoscopy helps to read the pattern of dilating of the pupil whether it is in the normal range or not.
Blood tests
Blood tests are performed to diagnose if there are any infections or not. It is also very advantageous to check that all genetic conditions are normal.
X-rays/Computed tomography/CT scan
In some cases, these methods are very productive to point out congenital cataracts as a result of any trauma. Using x-rays or CT scans gives a clearer picture of the brain or nervous system and helps to take further action accordingly.
Treatment of congenital cataracts
As discussed earlier, babies with congenital cataracts need special care and attention. Early diagnosis is very important because it can help to minimize the risk of blindness. That’s why ophthalmologists consider the first 72 hours very important. Following are some of the treatments:
Operation/Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment highly depends upon the density and the size of the cataract. If the magnitude of cataracts is high, it is necessary to remove the affected cloudy part of the eye in the baby.
The age of the baby is a very important factor to consider during this cataract removal surgical treatment. For optimum visual growth in babies and infants, the pediatric ophthalmologist recommends the age of 6 to 10 weeks is appropriate for this surgical treatment.
If this operation is performed at the younger age of the child, higher will be the risk of amblyopia.
Use of Contact/Intraocular lens
After the removal of cataracts, special kinds of contact lenses are used to rehabilitate normal vision. In some cataracts cases, Intraocular lenses (IOL) are also implanted in the eyes as per ophthalmologist recommendation. But in the case of infants and babies, specialists are still debating whether IOL should be used or not. Some young ones who are not comfortable with contact lenses, use glasses instead.
If the baby has mild or minor cataracts, ophthalmologists recommend coping with this situation with therapies and attention, and services for the affected child.
Patch therapy
This therapy is used if one eye is healthier than the other one. A special patch or piece is used to cover the healthier eye of your baby. The idea behind this therapy is to strengthen the signals between the affected eye and brain. This exercise is performed several times a day for a specific time as per the doctor’s advice. This therapy is time taking and remains in practice until the age of 8-10 when the weaker eye becomes stable.
Special Services/O&M Trainings
Children suffering from cataracts need special attention since their birth. For this purpose, parents should remain in contact with their pediatric ophthalmologist as well as with their local childhood assistance center.
These early intervention services improve the progress of the baby. These centers also provide orientation and mobility (O&M) training, which helps them promote their safety in their surrounding environment.
Conclusion
A congenital cataract is the cloudiness of the lens in the eye of infants which can lead to vision blurriness to blindness. Early diagnosis is key very vital in this disease. That’s why it is recommended to keep regular visits of your child to your ophthalmologist. There are many symptoms of congenital cataracts but in some cases, it is difficult to find any particular reason.
It is very tough to have a child with a congenital cataract. In case your child suffers from this disease, being a parent, your job will be going to be very challenging. You have to collect maximum data about the disease and remain in contact with your ophthalmologist to ensure a better future for your child with his disability.

The latest research and updates straight to your inbox !
Join our subscribers for exclusive access to our monthly newsletter related to optometry